- When are hydrogen hoses used?
- What do hose assemblies consist of?
- What materials are used in hydrogen hoses?
- What are the properties of hose assemblies?
- What connectors can be used in hydrogen hose assemblies?
- In what length can hose assemblies be used?
- What accessories are available for hydrogen hose assemblies?
- Is there an end-of-line test of the hose assemblies?
- What are the rated pressures and fields of application of high-pressure hydrogen hoses?
- What is the flow rate in hose assembly?
- According to which standards are high-pressure hydrogen hose assemblies tested?
Browse hydrogen hoses from leading suppliers on our marketplace!
When are hydrogen hoses used?
Hydrogen hoses are used in hose assemblies and are applied to convey hydrogen. In addition, they offer the advantage of flexibility compared to piping.
What do hose assemblies consist of?
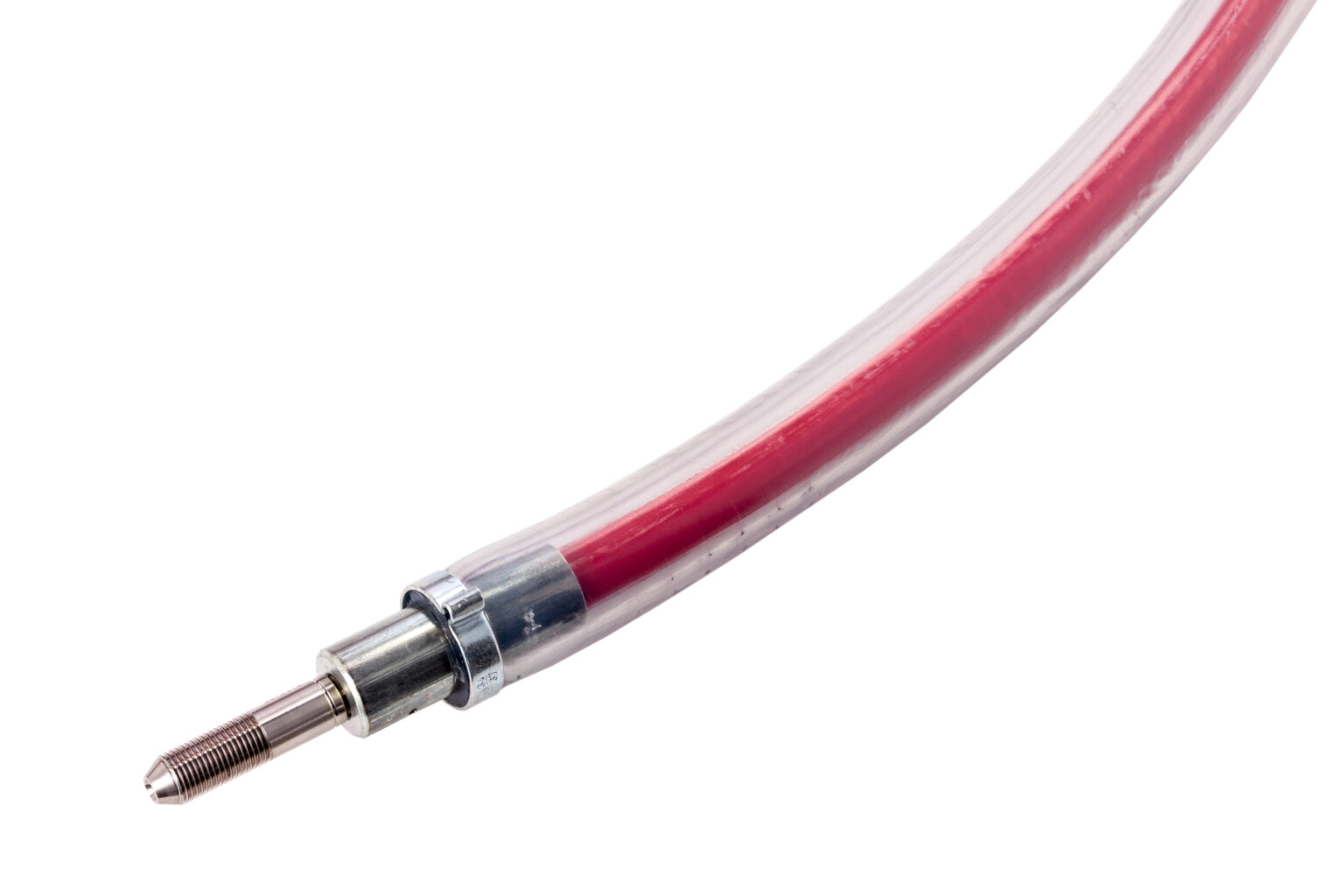
A hose assembly consists of a hose and a fitting at the respective hose end and is used as a connection element between various components. The size of a hose is defined by the indication of its nominal diameter (DN or ID) and refers to the inner diameter of the hose. The abbreviation “DN6” or “ID6”, for example, describes a hose with a nominal diameter of 6 mm.
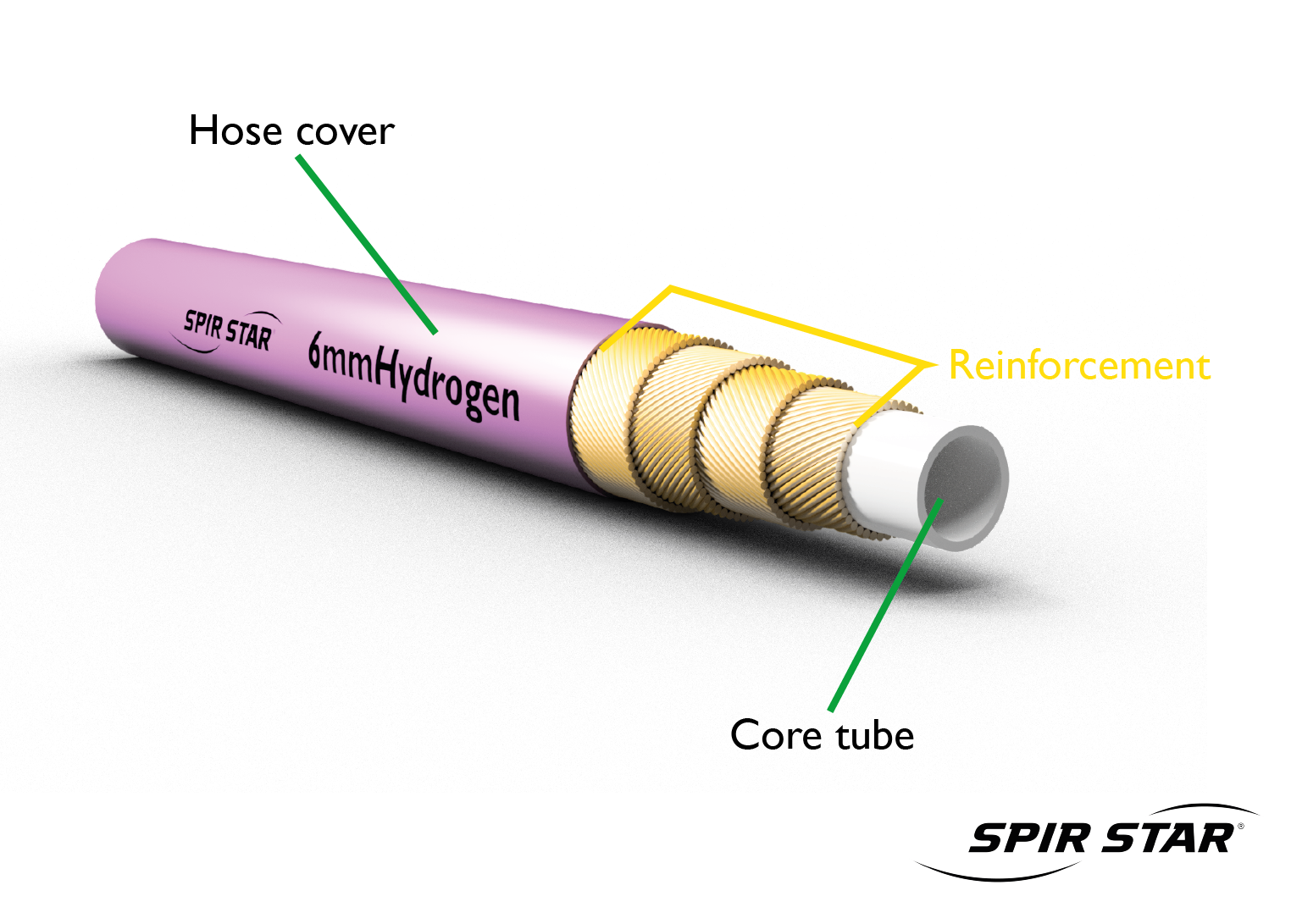
A high-pressure hydrogen hose is usually composed of a core tube, the reinforcement (braided or spiralized fibers/wires) and a hose cover.
The gaseous hydrogen flows through the core tube. It features a gastight wall made of a synthetic material. To ensure that the core tube can resist the required pressures, it is supported by a reinforcement. Depending on the pressure the hose is exposed to, the reinforcement consists of one or several layers. These layers mostly consist of spiralized wires/fibers and/or a fiber/wire braid.
As the external layer, the hose cover protects the hose construction against environmental influences.
Fittings usually consist of a nipple and a sleeve. Both components are mainly made of (stainless) steel. When the hose assembly is produced, a sleeve is placed on the hose and a nipple is pushed into the hose. By crimping the sleeve, one obtains a permanent and gastight connection between the hose and fitting.
What materials are used in hydrogen hoses?
All components (core tube, nipple) coming into contact with gaseous hydrogen must be resistant to it. The contamination of the gaseous hydrogen by these components must be excluded. Therefore, excellent chemical resistance is a prerequisite for the materials used.
The material of the core tube has to feature particularly low gas permeability but at the same time must be suitable for a wide range of service temperatures and operating temperatures. Electrical charge should be prevented. This is why special thermoplastic materials are frequently used here.
When metals are used, there is the risk of hydrogen embrittlement. For this reason, the use of hydrogen-resistant stainless steels for the fittings is mandatory. The entire fitting is also exposed to environmental influences. As a result, the metal materials used have to be corrosion resistant.
In order to protect the core tube and the reinforcement, the material of the hose cover has to feature excellent abrasion resistance, UV and ozone resistance as well as chemical resistance.
What are the properties of hose assemblies?
The hose and fitting have a maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP) which must never be exceeded. This pressure is marked on both the hose and the fitting. Fittings can have a lower MAWP than the hose used. In this case, the MAWP of the hose assembly is limited by the pressure marked on the fitting.
A hose assembly must only be used in the intended temperature range. The service temperature of the hose assembly must never fall below the minimum or exceed the maximum rated temperature.
The design of the hose always provides a safety factor between the MAWP and the burst pressure of a hose assembly. According to relevant standards, the minimum burst pressure of hose assemblies conveying gas must correspond to four times the MAWP.
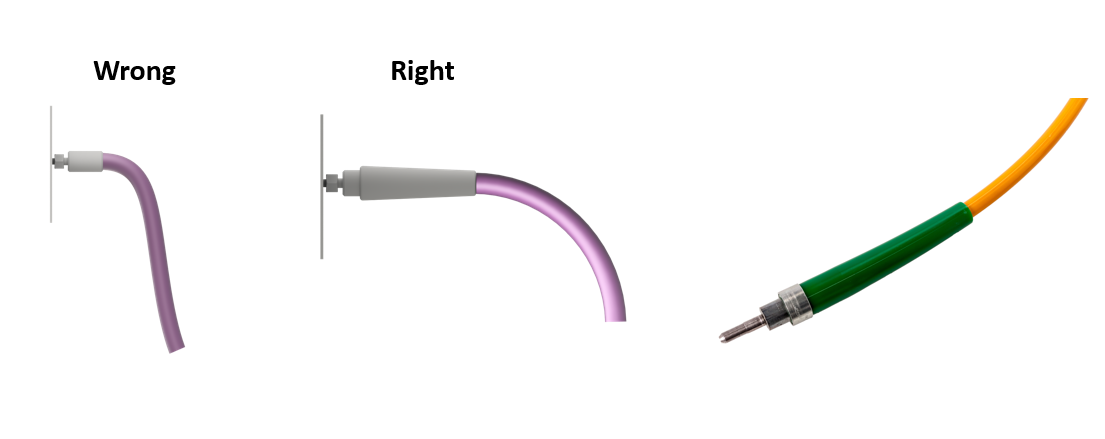
Hose assemblies do not feature unlimited flexibility. They have a minimum bend radius and should not be bent beyond it.
The manufacturer’s instructions regarding the storage conditions and storage time must be observed.
How long high-pressure hydrogen hoses can be used depends very much on the respective service conditions. This is the reason why it cannot be said in general how long a high-pressure hydrogen hose can be used.
For safety reasons, hose assemblies whose maximum allowable working pressure and/or minimum/maximum operating temperatures are unknown must never be used.
What connectors can be used in hydrogen hose assemblies?
In general, a great number of connector types can be used. So far, no standardized connector types have been defined which have to be used in hydrogen applications. This is why the connector type to be used mostly depends on the components to be connected. Consequently, it is also possible for a hose assembly to be equipped with two different types of connectors at the hose ends. As the geometry of the connector types is not standardized, it must be made sure that the female and male threads match to make a tight connection to the other components. The following connector types are commonly used:
- High pressure
- Medium pressure
- Type M
- JIC
- DKOS
In what length can hose assemblies be used?
High-pressure hydrogen hose assemblies are available in various customized lengths. When used for high mass flow rates, a long hose assembly will exhibit higher pressure losses – this needs to be taken into account in the design of a system.
What accessories are available for hydrogen hose assemblies?
Suitable accessories are available for hydrogen hose assemblies, which protect the hose assembly and thus increase its useful life. The following products are recommended:
1) Bend restrictor:
Prevents kinking of the hose behind the fitting.
2) Protection hose:
Serves as additional abrasion protection and reduces the impact of environmental influences.

3) Hose securing grip:
Retains the hose to prevent it from whipping. Whipping may occur e.g. due to a break of the fitting or its being torn out of the hose as a result of damage
4) Protective plugs:
Prevent the penetration of dirt and protect the thread when the hose assembly is not permanently connected.

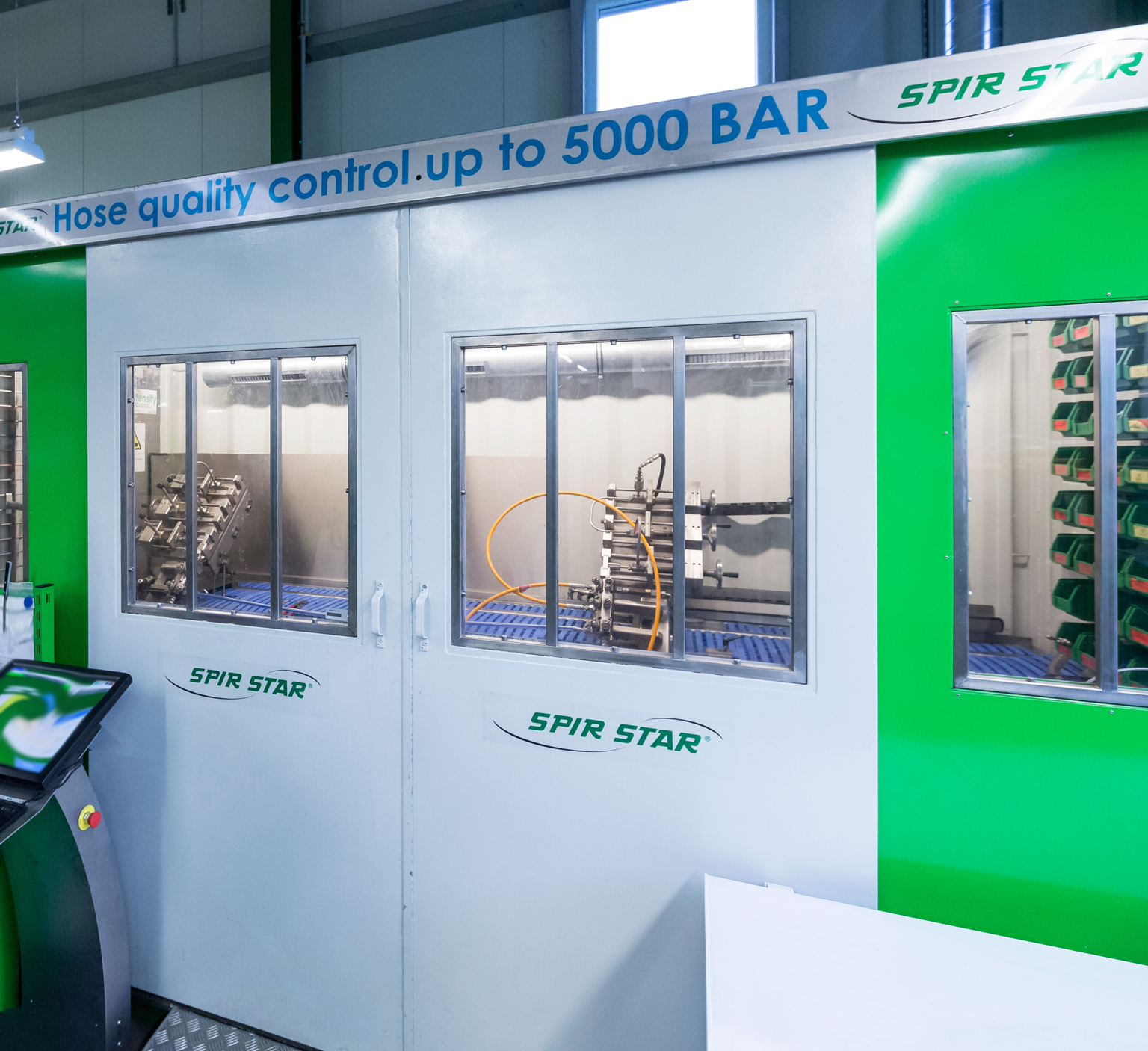
Is there an end-of-line test of the hose assemblies?
After the production of a hose assembly, the manufacturer performs a pressure test (usually with 1.5 times the maximum allowable working pressure) in order to ensure that there is a safe connection between the hose and fitting. Additionally, a gas-tightness test at maximum allowable working pressure can be performed after the pressure test in order to ensure that the hose assembly is gastight.

What are the rated pressures and fields of application of high-pressure hydrogen hoses?
In the hydrogen area, the pressure rating depends on the application. Hydrogen hoses can roughly be subdivided into low-pressure (<50 bar) and high-pressure applications (>200 bar). Low-pressure hydrogen hoses are frequently used in the following areas:
- Electrolyzers: connection from the electrolyzer to the compressor station
- Fuel cells: feed line in the vehicle
High-pressure hydrogen hoses are preferably used for the storage of hydrogen and/or the hydrogen infrastructure:
- Hydrogen trailers: filling / draining hose
- Hydrogen filling stations: dispenser hose
- Connection of high-pressure tanks
What is the flow rate in hose assembly?
The maximum possible mass flow rate in a hose assembly depends on the pressure loss occurring while the medium is being conveyed. When gas flows through a hose assembly, friction and changes of the cross section result in pressure loss. This is why pressure loss mainly depends on the inner diameter, the surface quality of the core tube and the length of the hose assembly. The larger the inner diameter and/or the shorter the hose assembly, the smaller the pressure loss. On the other hand, a larger inner diameter makes the hose assembly less flexible. For reasons of design, the inner diameter of the fitting is always smaller than the inner diameter of the hose. As the interaction of all features of the hose assembly results in pressure loss, a general statement regarding the maximum flow rate of a hose type is not possible.
According to which standards are high-pressure hydrogen hose assemblies tested?
Standards that ensure fitness for use and safety are essential for premium-quality hose assemblies. In standards, (inter-)national experts in a specific area determine the requirements for products.
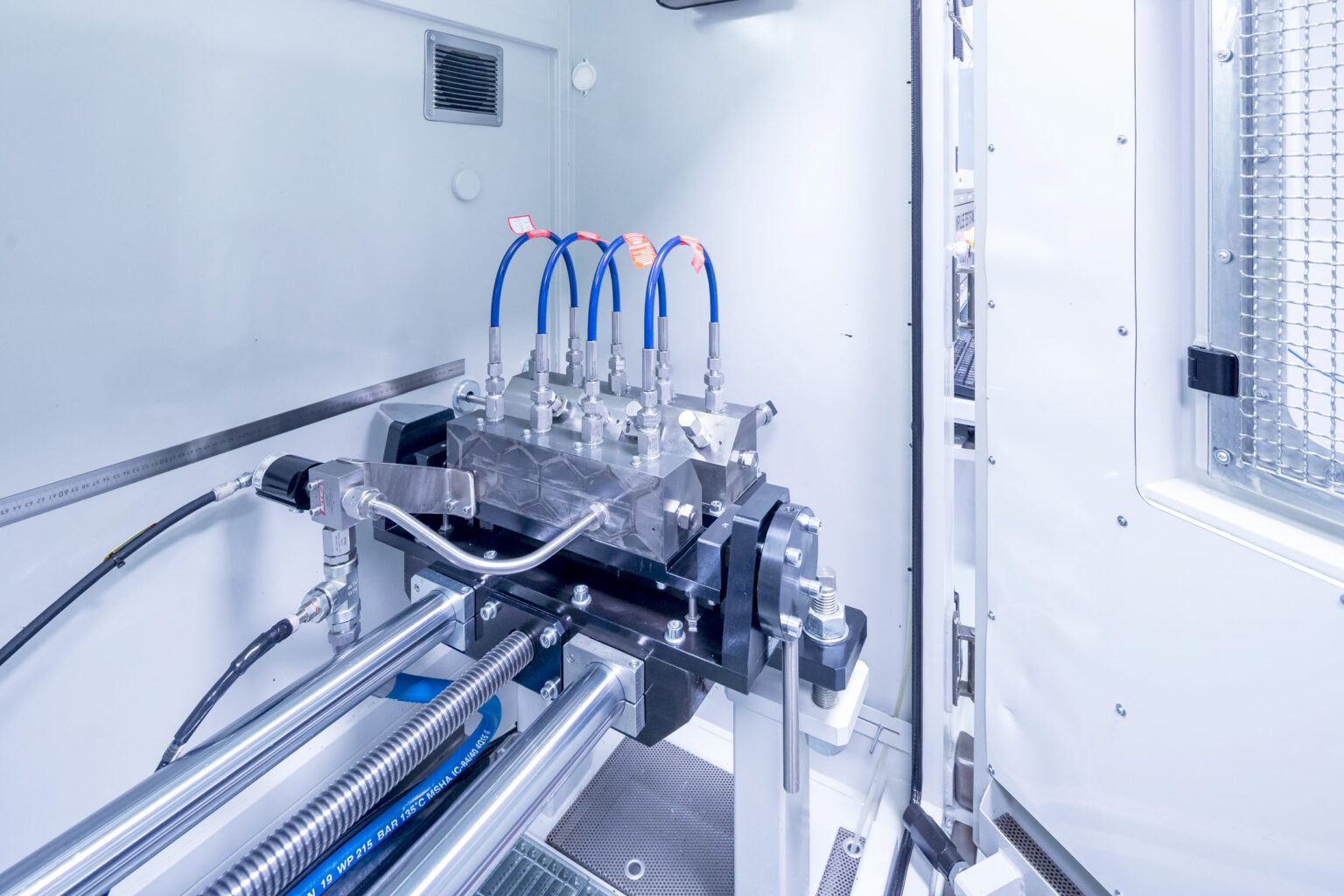

As a rule, hose assembly manufacturers perform at least the following tests with hose assemblies for the approval of a hose assembly type:
- Minimum bend radius test
- Burst pressure test
- Pressure test (at 1.5 times MAWP for 300 s)
- Tightness / Leakage test
- Pulse test (hydraulic stress reversal test at the temperature specified in the relevant standard)
- Tension test
Depending on the area of application, the relevant standards require tightened-up conditions and further tests. ISO 19880-5 is one of the best-known and most important standards for hydrogen hoses. It defines the requirements of refueling hoses on hydrogen dispensers. High-pressure hydrogen hoses certified to ISO 19880-5 have passed 18 different qualification tests. The following section lists the standards for high-pressure hydrogen hoses used for various applications:
a) Hydrogen dispenser hose:
- ISO 19880-5: Gaseous Hydrogen – Fueling stations – Part 5: Dispenser hoses and hose assemblies.
- CSA/ANSI HGV 4.2: Hoses for dispensing compressed gaseous hydrogen.
b) Hydrogen hoses in vehicles:
- CSA/ANSI HGV 3.1: Fuel system components for compressed hydrogen gas powered vehicles.
- ISO/CD 19887: Gaseous Hydrogen – Fuel system components for hydrogen fueled vehicles.
c) Hydrogen filling / draining hose on trailers or tanks:
- ISO 16964: Gas cylinders – Flexible hoses assemblies – Specification and testing
Content contributed by SPIR STAR
SPIR STAR AG, based in Rimbach-Mitlechtern, Germany, is an international leader in the manufacture of thermoplastic ultra-high-pressure hoses with spiralized reinforcement made of steel wire suitable for pressures ranging from 250 to 4,000 bar and with inner diameters ranging from 3 mm to 32 mm. Our hydrogen portfolio includes 3 hose types: 16mmHydrogen and 25mmHydrogen for trailer refueling and our ISO 19880-5 certified 6mmHydrogen for refueling of light-duty vehicles according SAE J2601.
Last update: 27.03.2023





