- What is a silicon fuel cell or silicon-based fuel cell?
- How are silicon based fuel cells manufactured?
- Please explain the composition of a silicon-based bi-polar plate
- Why are silicon-based bi-polar plates a revolutionary innovation?
- What are the advantages of silicon-based hydrogen solutions?
- How do silicon-based components improve the durability and reliability of fuel cells?
- How do silicon-based innovations optimize thermal and electrical management in fuel cells?
- How can silicon innovations reduce the overall cost of fuel cell production and operation?
- In what ways do silicon bipolar plates solve corrosion and degradation challenges?
- Which silicon-based hydrogen solutions can be built with silicon fuel cells
What is a silicon fuel cell or silicon-based fuel cell?
A fuel cell is an electrochemical device that converts the chemical energy of a fuel, most commonly hydrogen, and an oxidant, typically oxygen, directly into electrical energy through a controlled electrochemical reaction. This process generates electricity efficiently and cleanly, with water and heat as the primary byproducts. Fuel cells are considered a key technology for decarbonizing sectors such as heavy transportation, aviation, and power generation. However, widespread adoption remains constrained by challenges related to cost, durability, and system efficiency.
A silicon-based fuel cell refers specifically to a proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell stack that utilizes silicon bipolar plates in place of conventional metallic or graphite plates. The intrinsic material advantages of silicon, such as chemical inertness, high precision manufacturability, and excellent thermal stability, enable distinct differences in both system configuration and component integration. When combined with its highly-defined flow field architecture, the use of silicon results in a fundamentally different stack design approach, enhancing performance, reliability, and scalability.
How are silicon based fuel cells manufactured?
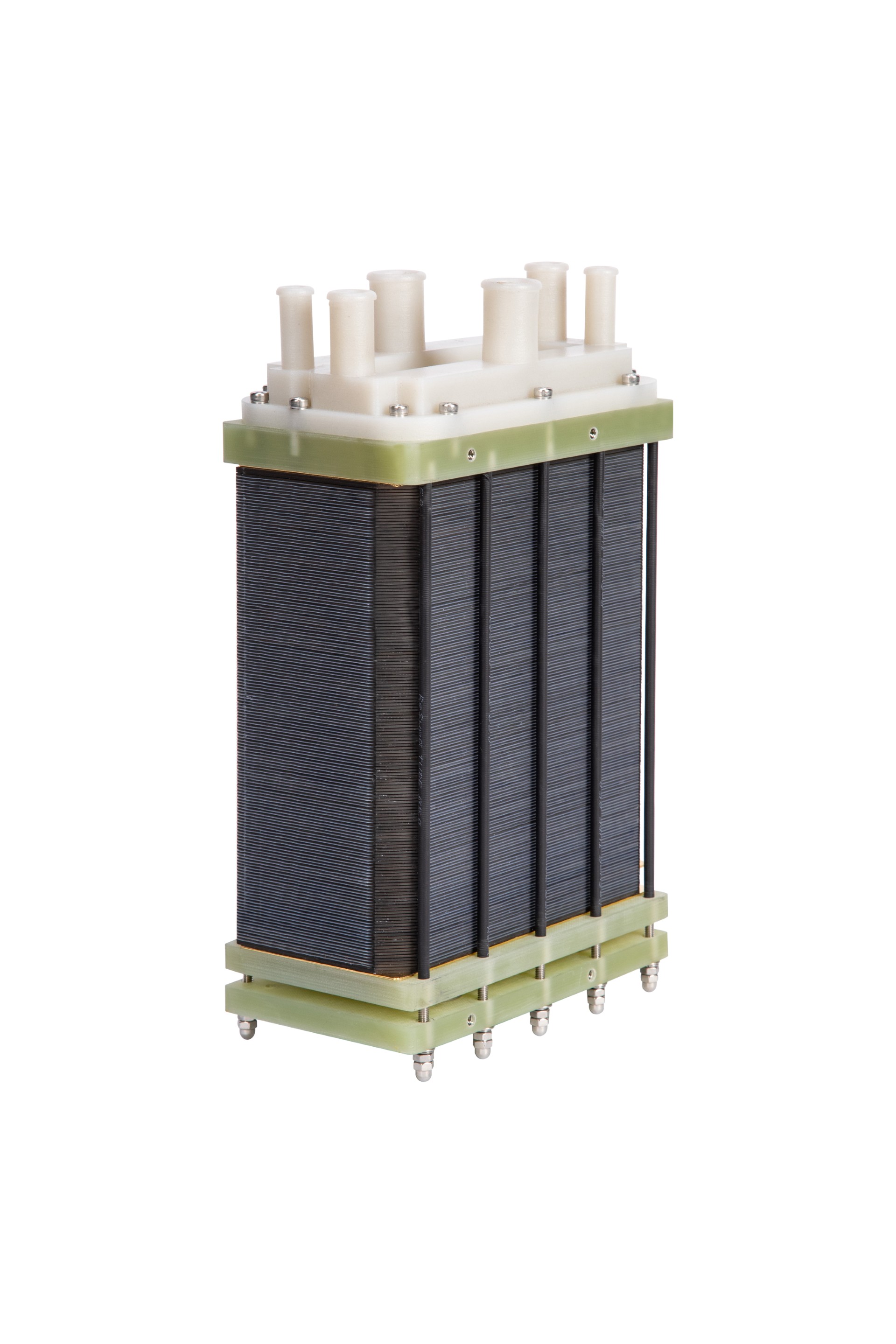
Fuel cells are typically assembled by stacking multiple single cells between two endplates that provide mechanical support and uniform compression. Each single cell consists of a membrane, electrocatalyst layers, gas diffusion layers (GDLs), and bipolar plates. The membrane, electrocatalyst layers, and GDLs are combined to form a membrane electrode assembly (MEA), which serves as the electrochemical core of the system and enhances the efficiency and compactness of the overall stack.
Silicon-based fuel cells follow the same general manufacturing process as conventional proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells, with the key distinction being the use of silicon bipolar plates in place of metallic or graphite counterparts. These silicon plates are fabricated from high-purity silicon wafers through a proprietary microfabrication process that draws on advanced manufacturing techniques from the semiconductor and solar industries. Once produced, the silicon plates are integrated into the stack using established industry-standard assembly methods, ensuring compatibility with existing fuel cell manufacturing workflows while delivering enhanced precision and performance.
Please explain the composition of a silicon-based bi-polar plate
Silicon-based bipolar plates are fabricated from monocrystalline silicon wafers, a material widely utilized in the photovoltaic and semiconductor industries. These wafers serve as the structural and conductive substrate for the plates. To enhance electrical conductivity, the silicon is doped with specific impurities, a well-established process in the solar industry that tailors the material’s electrical properties for optimal performance in fuel cell environments.
A silicon-based bipolar plate is formed by bonding together two monopolar plates, one configured for the hydrogen (anode) side and the other for the oxygen (cathode) side. Cooling channels are integrated on the reverse side of each monopolar plate during the bonding process, providing efficient thermal management within the stack.
A defining feature of silicon-based bipolar plates is their micron-scale flow channel architecture, which enables exceptional geometric precision and uniformity. This level of fine structural control surpasses that of traditional metal or graphite bipolar plates, resulting in improved fluid distribution, reduced pressure drop, and enhanced overall stack performance.
Why are silicon-based bi-polar plates a revolutionary innovation?
Silicon-based bipolar plates represent a fundamental advancement in the design and engineering of fuel cells and electrolysers, marking the first time that solar-grade silicon has been utilized as a structural and functional material within these systems. This innovation redefines the performance and scalability boundaries traditionally set by graphite and metallic bipolar plates.
Silicon intrinsically combines all the essential attributes required of a next-generation bipolar plate material. It offers exceptional mechanical strength, chemical inertness, and complete corrosion resistance in highly acidic and oxidative operating environments, conditions that often limit the lifespan and reliability of conventional materials. Beyond its robustness, silicon’s mature and cost-efficient supply chain, established through decades of semiconductor and photovoltaic production, provides a clear pathway toward mass manufacturing scalability and cost reduction.
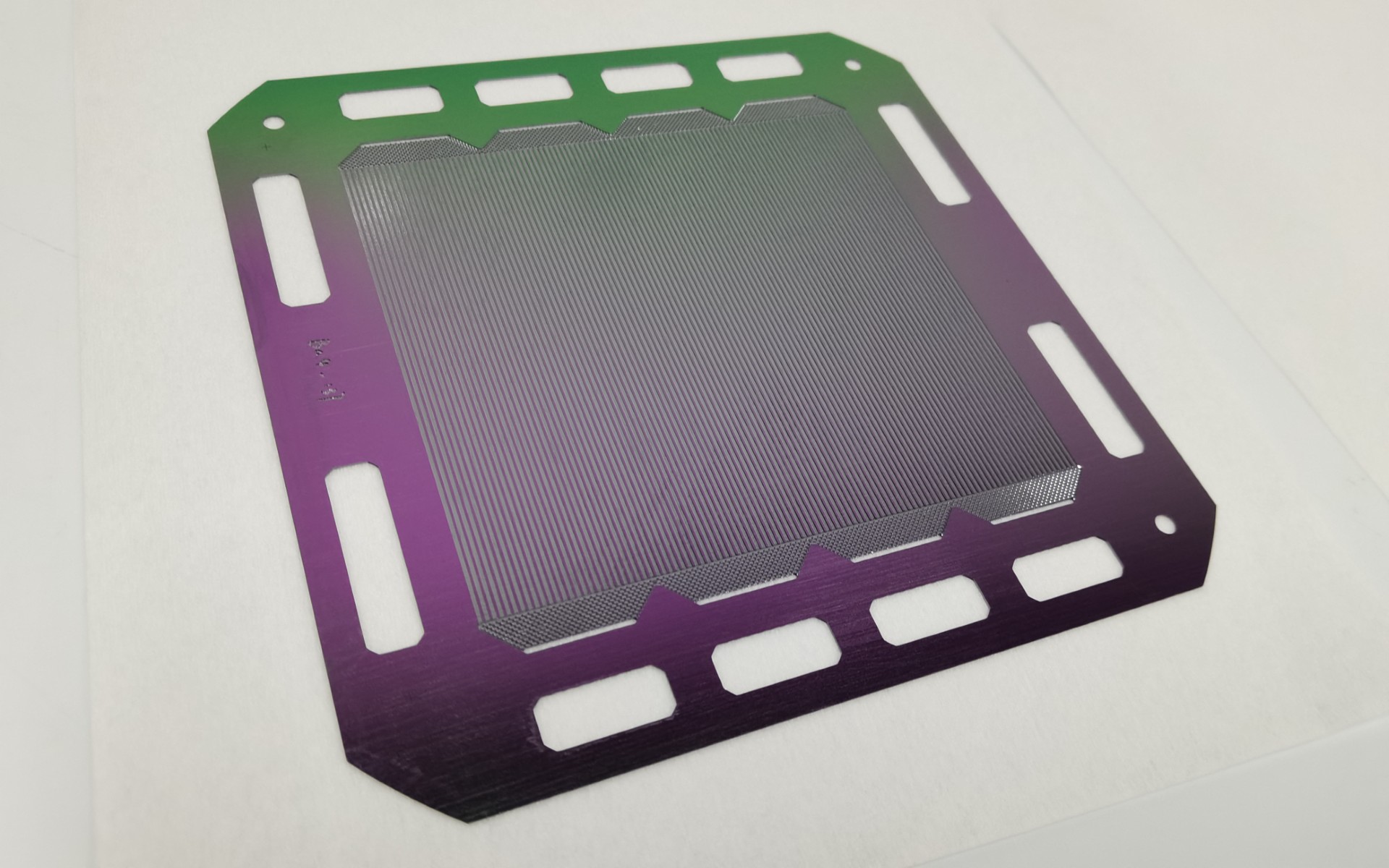
Perhaps most importantly, the crystalline precision of silicon enables the fabrication of micron-scale flow field geometries with unmatched dimensional accuracy. This level of precision allows for optimized reactant distribution, reduced parasitic losses, and enhanced thermal and water management across the stack. The result is a step change in electrochemical efficiency, durability, and design flexibility, positioning silicon-based bipolar plates as a transformative platform technology for the next generation of hydrogen fuel cells.
What are the advantages of silicon-based hydrogen solutions?
Silicon-based hydrogen solutions offer a distinct combination of material, performance, and manufacturing advantages derived from both the inherent properties of silicon and the maturity of the global silicon industry. Together, these factors enable a new generation of cost-effective, durable, and high-performance fuel cell and electrolyser systems.
Firstly, silicon’s abundance and established supply chain make it an economically and strategically attractive material. As the second most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, silicon benefits from decades of large-scale production infrastructure developed for the semiconductor and photovoltaic industries. This results in a highly optimized, low-cost, and globally distributed manufacturing ecosystem, enabling scalability and rapid deployment without the supply constraints that often affect specialty metals or graphite.
Secondly, the material properties of silicon deliver substantial performance benefits when integrated into hydrogen energy systems. Silicon exhibits exceptional chemical inertness, high thermal conductivity, and excellent electrical conductivity, characteristics that directly enhance the efficiency, stability, and longevity of fuel cells and electrolysers. In highly corrosive and humid operational environments, such as those within proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells, silicon remains chemically stable and resistant to degradation, eliminating the corrosion and leaching issues commonly observed with metallic bipolar plates.
Furthermore, silicon’s superior heat dissipation and electron transport characteristics contribute to improved overall stack efficiency and power density, while maintaining structural integrity over extended operating cycles. When combined with advanced microfabrication capabilities and scalable manufacturing processes, silicon-based hydrogen solutions present a transformative pathway toward high-efficiency, durable, and commercially viable clean energy systems.
Please find below a comparison between silicon bipolar plates over graphite or metallic bipolar plates based on key performance criteria.
| Silicon | Graphite | Metallic | |
| Efficiency | High | Mid | High |
| Lifetime (Hours) | 10,000+ | 10,000+ | 6,000 - 8,000 |
| Cost | Low | High | High |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | 120 | ~15 (composite) | 15-20 (Stainless Steel) |
| Mechanical Strength | 241 | 40-80 | ~500 |
|
Corrosion Resistance Anode Corrosion Currrent Density (µA/cm2) |
0.4 | <0.5 | 10 (Stainless Steel) |
Some information is unavailable publicly and the Company would not like to disclose in an article. In addition, some numbers on competitors are also unavailable.
How do silicon-based components improve the durability and reliability of fuel cells?
The durability and reliability of fuel cells are primarily influenced by the corrosion and chemical degradation of internal components, particularly the bipolar plates. In conventional designs, metallic bipolar plates are highly susceptible to corrosion due to the acidic, humid, and oxidative conditions within the fuel cell stack. Over time, this degradation can lead to ion leaching, oxidation, and surface passivation, all of which diminish electrical conductivity, impair electrochemical performance, and shorten the operational lifespan of the system.
Silicon-based components fundamentally overcome these challenges through the inherent chemical and structural stability of silicon. Silicon is naturally inert and exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, maintaining its structural and electrical integrity even in aggressive proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell environments. Unlike metallic materials, silicon does not form surface oxides or release contaminant ions, ensuring consistent performance throughout extended operational cycles.
Moreover, silicon bipolar plates do not require protective coatings or surface treatments to achieve corrosion resistance, reducing both manufacturing complexity and long-term failure risks associated with coating degradation. The result is a highly stable, low-maintenance component architecture that delivers superior long-term reliability, predictable performance, and extended system lifespan, even under demanding operating conditions.
How do silicon-based innovations optimize thermal and electrical management in fuel cells?
Effective thermal and electrical management are critical to ensuring the performance, efficiency, and longevity of fuel cell systems. The bipolar plates, responsible for conducting both heat and electricity, must exhibit high thermal conductivity to regulate stack temperature and high electrical conductivity to minimize resistive losses and maximize power output.
Silicon’s unique diamond-cubic covalent crystal structure provides it with exceptionally high thermal conductivity, enabling rapid and uniform heat dissipation throughout the stack. This property minimizes localized temperature gradients, prevents thermal stress-induced degradation, and enhances system reliability under high-load operation. The efficient heat transfer of silicon also reduces the complexity and cost of external cooling and thermal management subsystems, contributing to improved overall system efficiency.
Although silicon is inherently a semiconductor, its electrical conductivity can be precisely engineered through controlled doping, a process well-established in the semiconductor and solar industries. By introducing specific dopants, the electrical resistivity of silicon can be reduced to levels suitable for high-performance fuel cell applications. Consequently, silicon bipolar plates exhibit low contact resistance and high electron mobility, resulting in greater current density, improved power output, and reduced ohmic losses across the stack.

How can silicon innovations reduce the overall cost of fuel cell production and operation?
The cost of fuel cell technology remains a major barrier to widespread commercialization, driven primarily by expensive materials, limited manufacturing scalability, and operational inefficiencies. Silicon innovations address each of these factors through a combination of material abundance, manufacturing maturity, and system efficiency gains.
- Material Availability and Manufacturing Scalability: Silicon is the second most abundant element in the Earth’s crust and benefits from a well-established global supply chain supported by the semiconductor and solar industries. The production of silicon bipolar plates leverages existing industrial infrastructure and equipment, including wafer processing, doping, and bonding technologies. This reliance on proven, cost-efficient manufacturing processes ensures scalability, reduces capital investment requirements, and lowers the per-unit cost even at early production volumes.
- Elimination of Protective Coatings: Traditional metallic bipolar plates require expensive protective coatings, such as gold, titanium nitride, or carbon-based layers, to prevent corrosion in the acidic, humid fuel cell environment. Silicon’s natural corrosion resistance and chemical stability eliminate the need for such coatings, reducing both material and processing costs. The absence of coatings also simplifies manufacturing, shortens production cycles, and eliminates performance degradation associated with coating wear over time.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Lower Operational Costs: Silicon’s precision-engineered micron-scale flow channels enable optimized reactant distribution and water management, leading to improved electrochemical reaction efficiency. The resulting increase in power density and hydrogen utilization translates into reduced hydrogen consumption per unit of energy output, directly lowering operating costs.
In what ways do silicon bipolar plates solve corrosion and degradation challenges?
Corrosion and degradation are among the most significant failure mechanisms in conventional fuel cell stacks, directly affecting performance stability and system lifetime. Metallic bipolar plates are particularly vulnerable to electrochemical corrosion under the acidic, humid, and oxidative conditions characteristic of proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells. These reactions can result in surface oxidation, ion leaching, and electrical resistivity increases, all of which compromise fuel cell durability and efficiency.
In contrast, silicon’s intrinsic chemical inertness provides a decisive advantage. The strong covalent bonding within its crystalline lattice structure renders it highly resistant to corrosion, as it lacks the free electrons or ionic mobility that typically facilitate oxidative reactions in metals. Consequently, silicon bipolar plates maintain structural integrity and electrical conductivity without forming oxides or requiring surface protection.
This inherent corrosion resistance allows silicon-based systems to operate reliably under the most demanding conditions without degradation or performance drift. Moreover, by eliminating the need for protective coatings, silicon simplifies manufacturing, reduces long-term maintenance, and extends operational lifespan, solving one of the most persistent challenges in modern fuel cell technology.
Which silicon-based hydrogen solutions can be built with silicon fuel cells?
Silicon-based fuel cells are functionally compatible with all conventional proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell architectures, enabling their integration across a wide range of stationary and mobile applications. These include distributed power generation, and mobility solutions such as vehicles, drones, and aviation systems.
Due to their high power density and precise structural design, silicon-based fuel cells are particularly advantageous in applications with stringent weight, volume, and performance requirements, such as aerospace and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). The customizability of silicon microfabrication also enables the optimization of form factors, flow channel geometries, and thermal configurations for specific end-user needs or environmental conditions.
In addition to mobility applications, silicon’s durability and corrosion resistance make it ideally suited for stationary power systems, especially in remote or harsh environments where long operational lifetimes and low maintenance are essential. As a result, silicon-based fuel cell technology offers a versatile and scalable foundation for next-generation hydrogen solutions across both industrial and commercial sectors.
Content contributed by Siltrax Pty Limited
At Siltrax, we believe in hydrogen’s pivotal role in global decarbonization efforts. Our innovative silicon technology combines the studiness and reliability of silicon with industry leading MEAs to create an economical, high-performance solution. Siltrax was built on the vision of lowering the cost of hydrogen to make it accessible to all. Our low-cost hydrogen solutions will further decarbonization strategies and help to lead the charge towards a greener future.











